| page_type | description | languages | products |
|---|---|---|---|
Enumerates Plug-n-Play RS-232 devices that are compliant with the current revision of Plug and Play External COM Device. |
|

Serenum enumerates Plug-n-Play RS-232 devices that are compliant with the current revision of Plug and Play External COM Device. It loads as an upper filter driver to many different RS-232 device drivers that are compliant with its requirements and performs this service for them.
Open source hardware and software tools are very accessible this days, and a simple, inexpensive and open source FFT spectrum analyzer can be easily built using some of this tools. For this project, an Arduino Nano is used as the data acquisition system, it contains an USB to serial converter and ADC channels. HHD Software Free Serial Port Monitor - RS232/422/485 Communication Software Data Sniffer and Analyzer. Rs232 sniffer and analyzer for Windows free serial port analyzing software rs232 port data capture utility. Device driver or serial hardware development and offers the powerful platform for effective coding, testing and optimization. Com0com is open-source, so you could use that as a starting point. Another possible solution could be to pick up an rs232 splitter cable forks the serial signal to another serial port. Or yet another possibility is a Serial Sniffer program (or an open source sniffer ).
Serenum implements the Serenum service; its executable image is serenum.sys.
The Null-modem emulator is an open source kernel-mode virtual serial port driver for Windows, available freely under GPL license. The Null-modem emulator allows you to create an unlimited number of virtual COM port pairs and use any pair to connect one COM port based application to another. Devices in the second category are infinitely more flexible. These are BASIC- and C-programmable products that take on a role of SoI devices when loaded with our open-source SoI application. All Tibbo Serial-over-IP (SoI) products feature an Ethernet port as the standard means of networking.
Windows provides Serenum to support Serial and other serial port function drivers that need to enumerate an RS-232 port. Hardware vendors do not have to create their own enumerator for RS-232 ports. For example, a device driver can use Serenum to enumerate the devices that are attached to the individual RS-232 ports on a multiport device. Free software serial port monitor, Com Rs232 sniffer with communication packet data analyzer. This monitoring utility can spy, capture, view, analyze, test com ports activity performing com port connection and traffic analysis with data acquisition and control. Research the functionality of any third-party software and hardware, testing.
Serenum is an upper-level device filter driver that is used with a serial port function driver to enumerate the following types of devices that are connected to an RS-232 port:
- Plug and Play serial devices that comply with Plug and Play External COM Device Specification, Version 1.00, February 28, 1995.
- Pointer devices that comply with legacy mouse detection in Windows.
The combined operation of Serial and Serenum provides the function of a Plug and Play bus driver for an RS-232 port. Serenum supports Plug and Play and power management.
Windows provides Serenum to support Serial and other serial port function drivers that need to enumerate an RS-232 port. Hardware vendors do not have to create their own enumerator for RS-232 ports. For example, a device driver can use Serenum to enumerate the devices that are attached to the individual RS-232 ports on a multiport device.
File Manifest
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| Enum.c | Functions that enumerate external serial devices (the main purpose of this driver) |
| Pnp.c | Plug and Play support code |
| Power.c | Power support code |
| Serenum.c | Basic driver functionality |
| Serenum.h | Local header with defines, prototypes |
| String.c | String handling support; mainly ASCII to UNICODE functionality |
| Serenum.rc | Resource script |
For more information, see Features of Serial and Serenum.
| Status | supported |
|---|---|
| Source code | openbench-logic-sniffer |
| Channels | 32 |
| Samplerate | 200MHz |
| Samplerate (state) | ? |
| Triggers | ? |
| Min/max voltage | -0.5 to +7V (buffered), 0-3,3V? (unbuffered) |
| Memory | 24ksamples |
| Compression | RLE (optional) |
| Website | dangerousprototypes.com |
The Openbench Logic Sniffer (OLS) is an FPGA-based logic analyzer, supporting 32 probes for probing up to 100MHz signals and advanced trigger functionality. It is a fully open source device — the circuit design, VHDL code for the FPGA, firmware for the PIC microcontroller and Java-based client software are all freely available. The project is a collaboration between Gadget Factory and Dangerous Prototypes.
The device started life as the Sump Logic Analyzer, which was meant to be run on a Digilent FPGA development board. The Openbench Logic Analyzer unit is a custom-designed board with low cost in mind: it can be bought for $45 from Seeed Studio.
Communication between the board and the PC is done via a USB port connected to a PIC 18F24J50 microcontroller, which presents a standard USB ACM profile. The host handles this as a serial port. The default maximum serial speed of the SUMP Java client is 115200bps, but the USB ACM virtual serial port can be opened at much higher speeds. An overview of the endpoint profile is at Openbench Logic Sniffer/Info.
Full OLS info: dangerousprototypes.com: Open Bench Logic Sniffer
Status:
The sigrok driver does not currently support the 'serial' trigger mode. This allows a single trigger to be set (on one or more probes), but with up to 32 stages. The parallel mode is supported, which supports up to 4 distinct trigger stages on any probe.
200MHz demux mode will not work right now, since the driver always expects 32-bit sample values.
Recent hardware (from seeedstudio at least) appears to ship with an FPGA loaded that doesn't support fetching metadata from the device, and causes pulseview to exit with 'Caught exception: not applicable' when trying to connect to the device. The source and / or version number of this FPGA core is unknown, if you have purchased a new device and have this problem then you probably want to load the 3.07 demon core to the FPGA using ols-fwloader.
- 4Protocol
Hardware
- Xilinx Spartan XC3S250E
- Microchip PIC18F24J50-I/30
- Atmel 0952 450B0410 SU or Winbond 25X40 in later versions (see notes below on firmware update tools)
- ON Semiconductor LCX16245
Software tools
- Java logic sniffer client []
- Update packages [1]
- FPGA / PIC firmware updater ols-fwloader - required for later boards with alternative FPGA ROM memory
Photos
Device, front
Device, back
Device with buffer 'wing'
Protocol
The communications protocol between the board and the PC is below, taken from the original Sump documentation.
All communication is done using a standard RS232 connection with 8 data bits, 1 stop bit and no parity. The transfer rate is not emulated over USB and can be set to any speed supported by the operating system. Pump-loader, an update utility for the Logic Sniffer ROM chip, uses 921600bps by default. XON/XOFF software flow control is available.
When sending captured data the analyzer will send blocks of four bytes, the first containing the lowest channels. No start or end sequence exists. The host can assume an end of transmission if no data has been received for the duration of one byte.
The protocol used by hardware version 0.5 and older is not covered here. Hardware 0.6 uses protocol version 0, and hardware 0.7 uses protocol version 1. Unless otherwise stated, commands exist in both versions.
The following list provides a short overview of commands understood by the analyzer.
Short Commands
These commands are exactly one byte long.
Reset (0x00)
- Resets the device. Should be sent 5 times when the receiver status is unknown. (It could be waiting for up to four bytes of pending long command data.)
Run (0x01)
- Arms the trigger.
ID (0x02)
- Asks for device identification. The device will respond with four bytes. The first three ('SLA') identify the device. The last one identifies the protocol version which is currently either '0' or '1'.
XON (0x11)
- Put transmitter out of pause mode. It will continue to transmit captured data if any is pending. This command is being used for xon/xoff flow control.
XOFF (0x13)
- Put transmitter in pause mode. It will stop transmitting captured data. This command is being used for xon/xoff flow control.
Long Commands
Are five bytes long. The first byte contains the opcode. The bytes are displayed in the order in which they are sent to the serial port starting left. The bits within one byte are displayed most significant first.
Set Trigger Mask (0xc0, 0xc4, 0xc8, 0xcc)
- Defines which trigger values must match. In parallel mode each bit represents one channel, in serial mode each bit represents one of the last 32 samples of the selected channel. The opcodes refer to stage 0-3 in the order given above. (Protocol version 0 only supports stage 0.)
Set Trigger Values (0xc1, 0xc5, 0xc9, 0xcd)
- Defines which values individual bits must have. In parallel mode each bit represents one channel, in serial mode each bit represents one of the last 32 samples of the selected channel. The opcodes refer to stage 0-3 in the order given above. (Protocol version 0 only supports stage 0.)
Set Trigger Configuration (0xc2, 0xc6, 0xca, 0xce)
- Configures the selected trigger stage. The opcodes refer to stage 0-3 in the order given above. The following parameters will be set:
- delay
- If a match occures, the action of the stage is delayed by the given number of samples.
- level
- Trigger level at which the stage becomes active.
- channel
- Channel to be used in serial mode. (0-31 in normal operation; 0-15 when demux flag is set)
- serial
- When set to 1 the stage operates as serial trigger, otherwise it used as parallel trigger.
- start
- When set to 1 a match will start the capturing process. The trigger level will rise on match regardless of this flag. (Command available as of protocol version 1.)
- delay
Set Divider (0x80)
- When x is written, the sampling frequency is set to f = clock / (x + 1).
Set Read & Delay Count (0x81)
- Read Count is the number of samples (divided by four) to read back from memory and sent to the host computer. Delay Count is the number of samples (divided by four) to capture after the trigger fired. A Read Count bigger than the Delay Count means that data from before the trigger match will be read back. This data will only be valid if the device was running long enough before the trigger matched.
Set Flags (0x82)
- Sets the following flags:
- demux
- Enables the demux input module. (Filter must be off.)
- filter
- Enables the filter input module. (Demux must be off.)
- channel groups
- Disable channel group. Disabled groups are excluded from data transmissions. This can be used to speed up transfers. There are four groups, each represented by one bit. Starting with the least significant bit of the channel group field channels are assigned as follows: 0-7, 8-15, 16-23, 24-31.
- external
- Selects the clock to be used for sampling. If set to 0, the internal clock divided by the configured divider is used, and if set to 1, the external clock will be used. Filter and demux are only available with internal clock.
- inverted
- When set to 1, the external clock will be inverted before being used. The inversion causes a delay that may cause problems at very high clock rates. This option only has an effect with external set to 1.
- demux
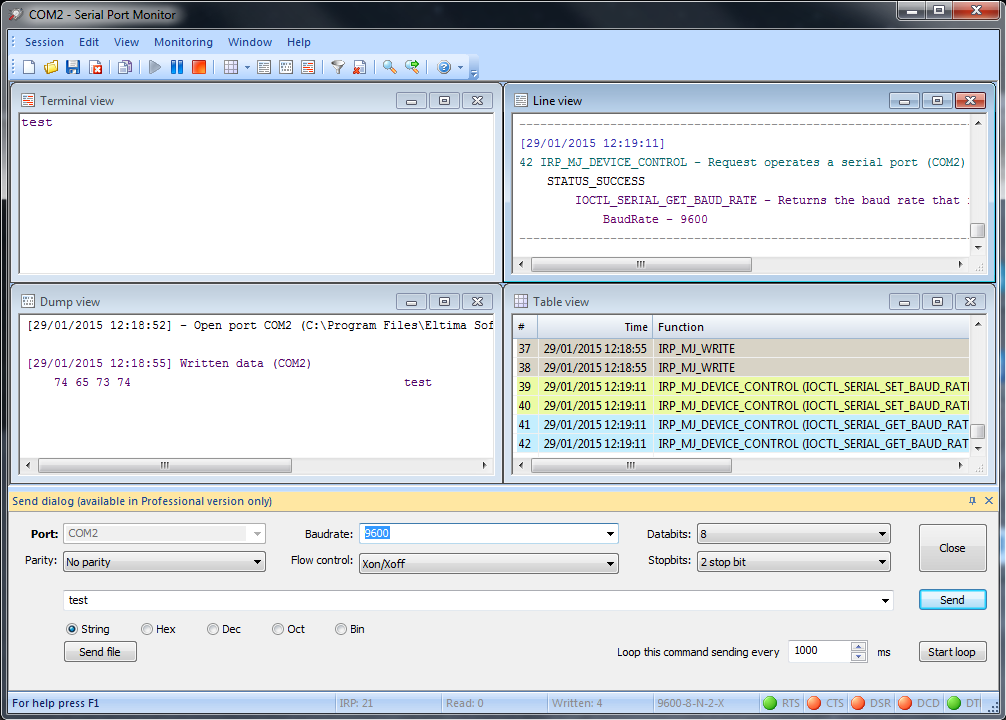
Open Source Serial Port Monitor
Known Bugs
RLE mode is currently broken due to samples count being passed in from sigrok is the total samples we will receive, but however the OLS sees this as compressed samples so in turn we can never know how many samples will get send back. Even worse since the buffer is sent backwards you are likely to lose all the data you are trying to trace at the beginning of the session.
Resources
Serial Port Monitor
- Open Bench Logic Sniffer (main wiki page)



